The body’s natural building block
Collagen is a protein that acts as the body's natural building material, giving structure and strength to skin, bones, muscles, and connective tissues. It’s often described as the glue that holds us together. Our bodies produce collagen naturally, but production slows as we age, which is why many people look to collagen-rich foods or supplements to support skin elasticity, joint comfort, and overall tissue health.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and a fundamental structural component of connective tissues. It serves as a building block for skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and blood vessels. In fact, collagen makes up around 30% of the body’s total protein content, underscoring its essential role in maintaining strength, flexibility, and resilience.
Structure and composition
Collagen belongs to a family of fibrous proteins characterized by a unique triple-helix structure. Each collagen molecule consists of three polypeptide chains (known as alpha chains) wound tightly together, creating a strong and stable configuration. This helical structure is rich in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline - amino acids critical for stability and function.
When many collagen molecules assemble, they form fibrils that bundle into fibers, providing tensile strength and elasticity to tissues. This molecular architecture explains why collagen is so durable and resistant to stretching forces.
Types of collagen
To date, scientists have identified at least 28 different types of collagens, though types I, II, and III are the most prevalent:
- Type I – the most abundant, found in skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
- Type II – primarily located in cartilage, providing cushioning and flexibility in joints.
- Type III – supports the structure of muscles, blood vessels, and organs.
Other types have more specialized roles, such as forming basement membranes (type IV) or anchoring fibrils in skin (type VII).
Collagen in industry
- Due to its abundance and functional properties, collagen has wide applications across industries:
- Food and nutrition – Collagen and collagen peptides (hydrolyzed collagen) are used in functional foods and dietary supplements to support skin health, joint function, and muscle recovery.
- Biomedical field – Collagen is utilized in wound dressings, tissue engineering, and drug delivery systems because of its biocompatibility.
- Cosmetics – Topical products often feature collagen for its hydrating and film-forming benefits.
Collagen is more than just a structural protein – it is a key player in maintaining the integrity and function of biological tissues. Its unique triple-helix design, diversity of types, and biological functions make it indispensable to human health. At the same time, its versatility has made it a valuable ingredient in food, health, and medical applications.
Popularity in mainstream nutrition
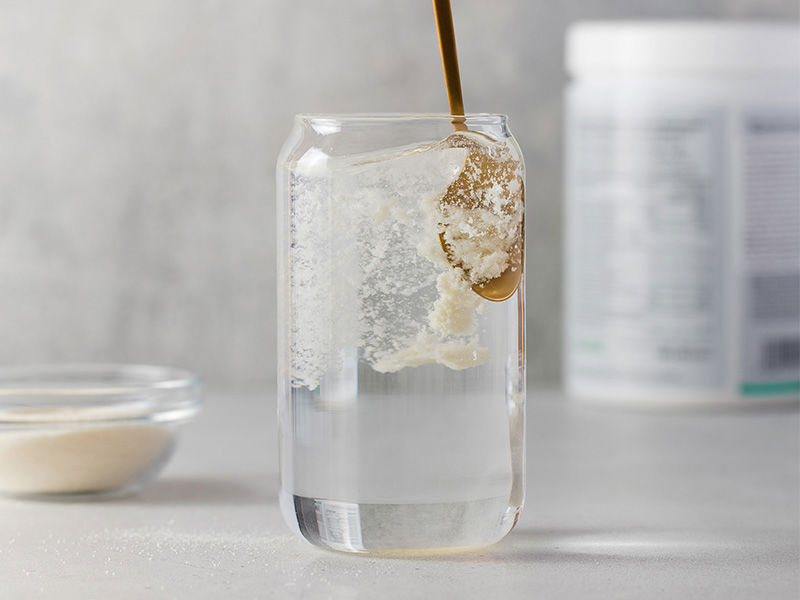
Collagen continues to expand across key food and beverage categories, moving well beyond traditional supplements as brands tap into its versatility and broad consumer appeal, including the demand for indulgence. The rising number of new product launches highlights collagen’s ability to integrate seamlessly into everyday formats - from beverages, bars, and snacks to dairy, bakery, and functional foods. This momentum reflects growing consumer interest in proactive nutrition, healthy aging and convenient ways to support overall wellness, while giving manufacturers a flexible ingredient that enables ongoing innovation across both established and emerging applications.
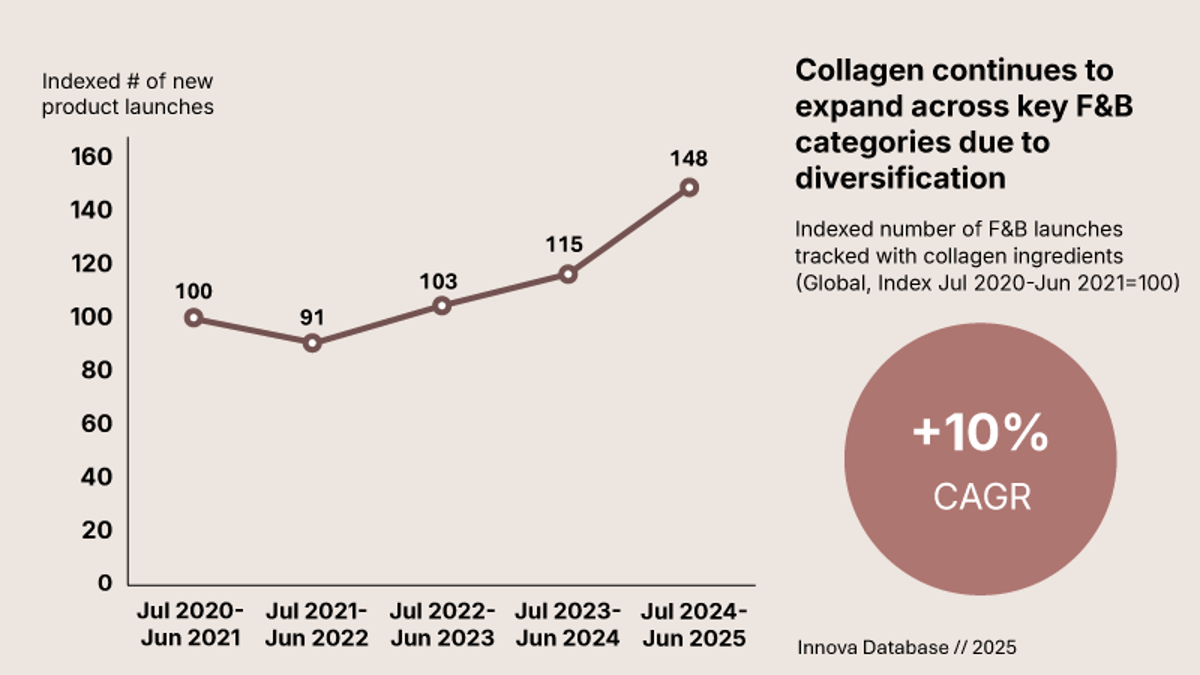
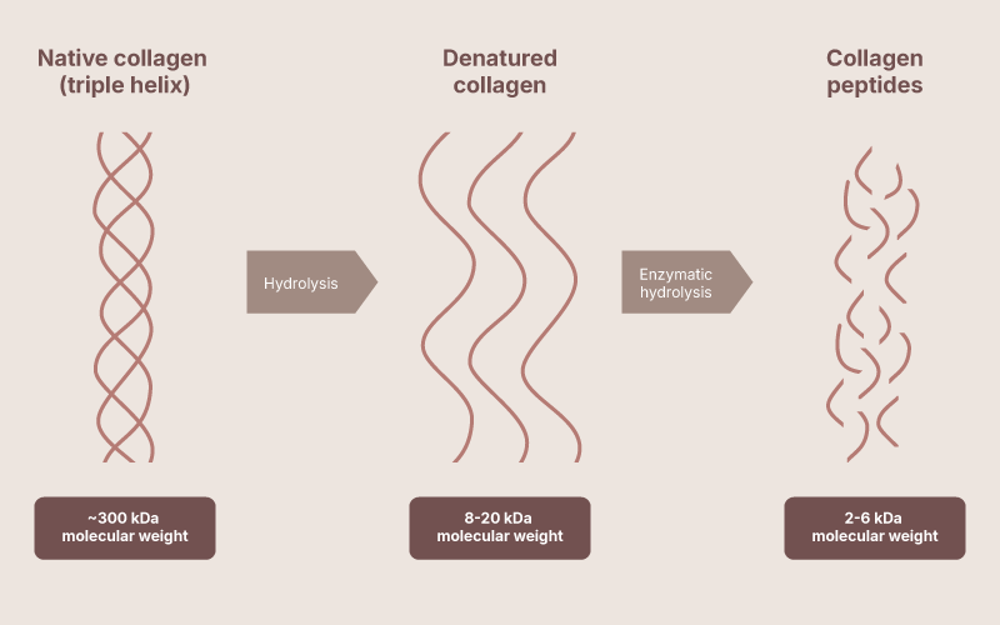
Why collagen peptides
Collagen peptides like our OmniCol™ are short chains of amino acids derived from collagen, the most abundant protein in the body. They are highly bioavailable, meaning they are easily absorbed and utilized by the body to support the synthesis of new collagen in skin, joints, and connective tissues. Their neutral taste, excellent solubility, and heat stability make them ideal for inclusion in a wide range of functional food and beverage applications, combining condition-specific benefits with everyday enjoyment.
We are here to help
Essentia manufactures a wide range of clean label nutritional ingredients derived from first-rate animal-based raw materials including OmniCol™. These ingredients are ideal for manufacturers looking to tap into the growing demand for functional food and beverage solutions.
Let us help you meet consumer needs
Get in on the rising market that caters to consumers who prefer nutrition and specifically, collagen enriched foods. Co-create with knowledgeable experts in Essentia’s innovation center; to find out how 100 % natural clean label ingredients can elevate your brand. The applications division will work with you to explore the optimal custom solutions that suit your needs, to help find the desired nutritional profile for your products. Get in touch with your local Essentia representative today to explore how we can co-create and support your success!




